Remote Tracing
As malware analysis is often performed in environments with limited GPU access, rgat provides the ability to perform tracing and visualisation on separate devices in real time, by passing trace data to the visualiser over a network connection.
Usage
- Note: Remote tracing is still quite unstable and is next on the list of things to work on *
rgat should be started in GUI mode as usual on the visualiser device, and in headless ‘bridged’ mode on the tracing device. To support different network configurations, remote tracing connection can be established in either direction.
rgat should be installed on the ‘headless’ tracing device (running in command line mode) and the GPU enabled analysis device (running in GUI mode). Signatures can be transferred by the GUI to the tracer, but actual samples need to be managed by the user.
Method 1: GUI -> Headless connection
On the tracing device: * Run rgat.exe on the command line * Use the -i option to specify an interface [-i with no parameters prints a list] * Use the -p option to specify aport to listen on * Provide a pre-shared key with -k, which can be omitted if already configured
On the analysis device, in the GUI:
* Click 'Local Mode' in the menu bar
* Click the 'Connect Mode' tab
* Enter the appropriate key, address:port and interface
* Click the Connect toggle
Method 2: Headless -> GUI connection
On the analysis device, in the GUI:
- Click ‘Local Mode’ in the menu bar
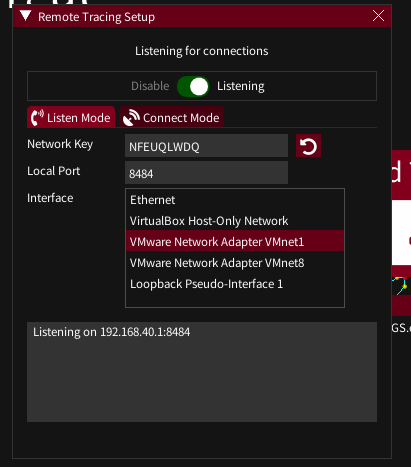
- Click the ‘Listen Mode’ tab
- Enter the appropriate key, port and interface
- Click the ‘Start Listening’ toggle
On the tracing device: * Run rgat.exe on the command line * Use the -i option to specify an interface [-i with no parameters prints a list] * Provide a pre-shared key with -k, which can be omitted if already configured * Use the -r option to specify and address and port
Security notes
- Only one connection can be active at a time.
- Connections can only be made GUI<->Headless, not GUI<->GUI or Headless<->Headless.
- The pre-shared key is used for ChaCha20 encryption.
- Listen mode will deactivate if an incorrect key is provided, to avoid brute forcing.
- Remote tracing will be deactivated (and must be reactivated to resume) if either party disconnects or any bad data is received. It is not intended to run as a long-term service.
- Anyone with the pre-shared key can execute arbitrary code on the listening device, so standard key choice and management caveats apply.
- Remote tracing is designed to facilitate analysis between Host<->VM or machines on a private analysis network, not over the internet.
- When connected in GUI mode, rgat will refuse to execute any processes, so remote and local tracing cannot be mixed.
As rgat is intended to execute arbitrary malicious code, the GUI in remote tracing mode has been designed to treat incoming data as radioactive. It’s still early in development though, so weigh up the risks accordingly.